Home
/
Methylcellulose
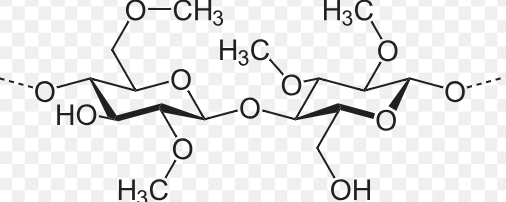
Methylcellulose
Methylcellulose (MC) has a backbone of repeating glucose units from cellulose, but with some hydroxyl (-OH) groups replaced by methyl groups (-CH₃) through etherification, making it water-soluble and giving it unique properties like thermal gelation (forming a gel when heated and dissolving when cooled). Its structure features varying degrees of substitution (DS), affecting its solubility and viscosity, and it's used as a thickener, stabilizer, and binder in food, pharma, and cosmetics
| CAS No. | 9004-67-5 |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | |
| Molecular Formula | C₂₀H₃8O₁₁ |
